3D Images
Translation
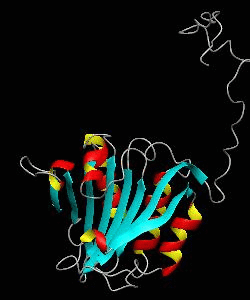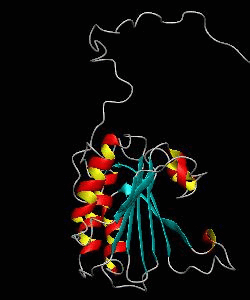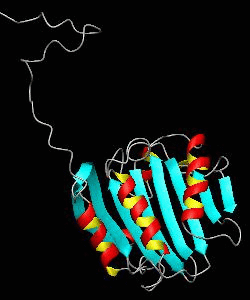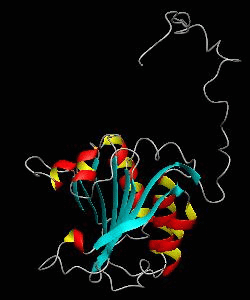
eIF4E
eIF4E, the mRNA cap binding protein, is a master switch that controls eukaryotic translation.We have solved the structure of the yeast eIF4E/m7Gpp complex in a CHAPS micelle.
eIF1
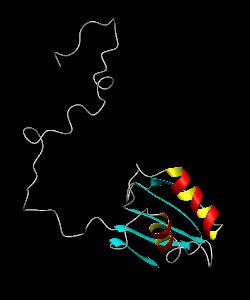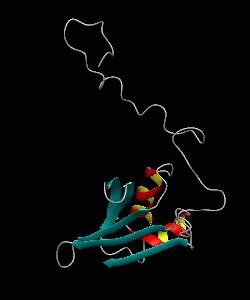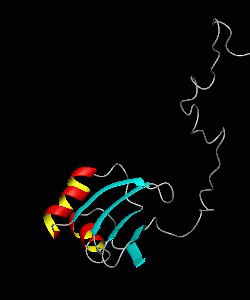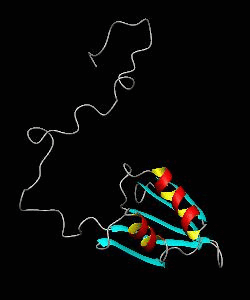
eIF1 is a universally conserved translation factor that is necessary for scanning and involved in initiation site selection. We have determined the solution structure of human eIF1 with an N-terminal His tag using NMR spectroscopy. The fold is new but similar to that of several ribosomal proteins and RNA-binding domains.
Transcription
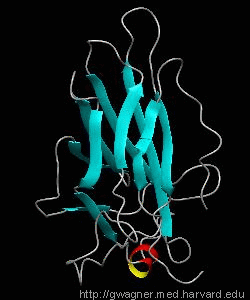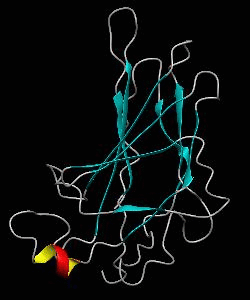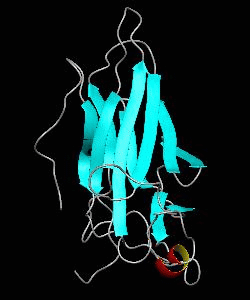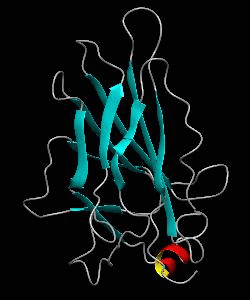
NFATc1
The nuclear factor of the activated T cell (NFAT) family of transcription factors regulates cytokine gene expression by binding to the promoter/enhancer regions of antigen-responsive genes. Here is the binary complex formed between the core DNA-binding domain of human NFATC1 and the ARRE2 DNA site from the interleukin-2 promoter.
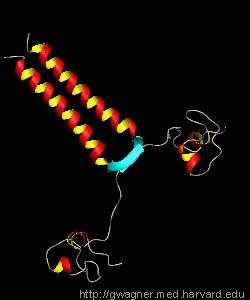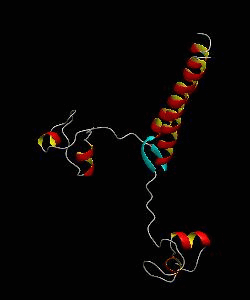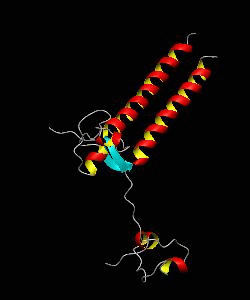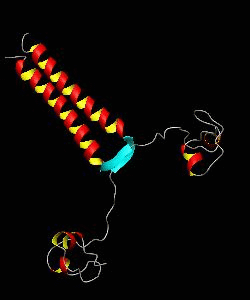
PUT3
The solution structure and backbone dynamics of the transcriptional activator PUT3 (31-100) has been characterized using NMR spectroscopy. PUT3 (31-100) contains three distinct domains: a cysteine zinc cluster, linker, and dimerization domain. The cysteine zinc cluster of PUT3 closely resembles the solution structure of GAL4, while the dimerization domain forms a long coiled-coil. A comparison of the structural elements provides a model for the DNA binding specificity of this protein.
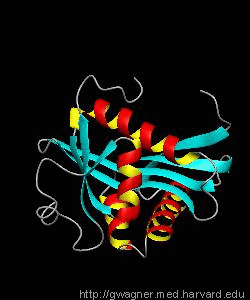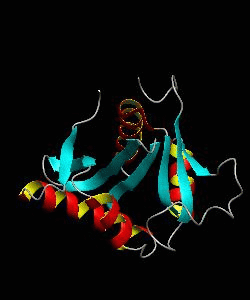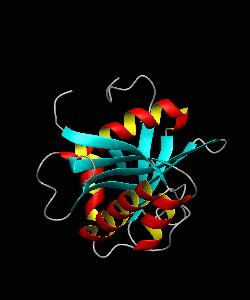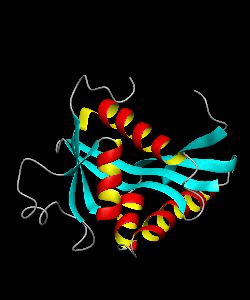
GCN5
Gene transcription requires the release of inactive DNA from its packaging of histone proteins. Yeast GCN5 is recruited to the promoter and causes hyper-acetylation of histones and transcriptional activation of target genes. Here we present the solution structure of the catalytic domain of the GCN5 histone acetyltransferase (residues 47-210) in complex with coenzyme A.
Apoptosis
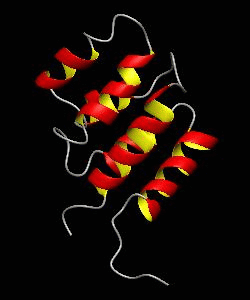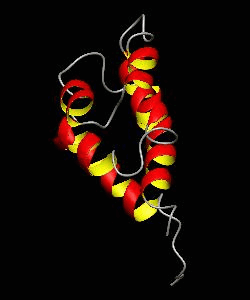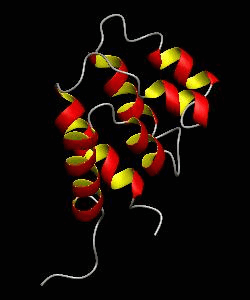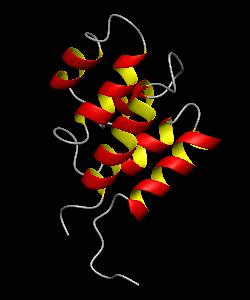
RAIDD-CARD
Apoptosis requires recruitment of caspases by receptor-associated adaptors through homophilic interactions between the CARDs (caspase recruitment domains) of adaptor proteins and prodomains of caspases. Here is the CARD structure of the RAIDD adaptor protein that recruits ICH-1/caspase-2.
Immunology
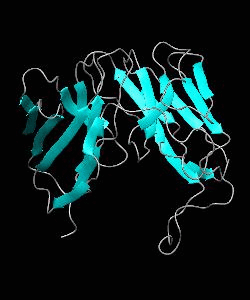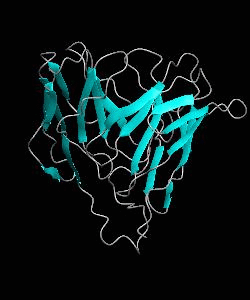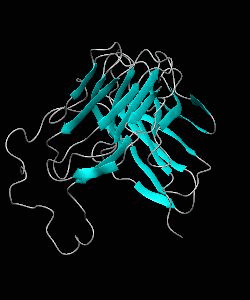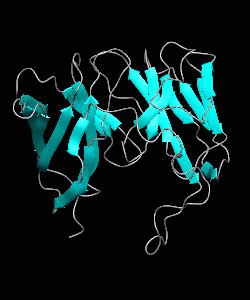
D10-scTCR
Using NMR spectroscopy, we determined the solution structure of a single-chain T-cell receptor (scTCR) derived from the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II-restricted D10 TCR.We infer a conserved orientation for TCR V(alpha) domains in complexes with both class I and II MHC-peptide ligands, which implies that small structural variations in V(alpha) confer MHC class preference.

1dCD2
Cell surface receptors, such as CD58 and CD2, are responsible for faciliating immune responses. Here is the NMR structure of the adhesion domain of CD2, which adopts an immunoglobulin V-set fold, with the binding face to CD58 facing the front.
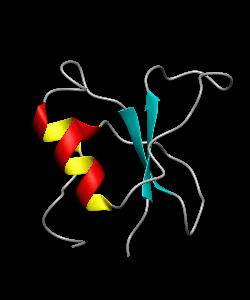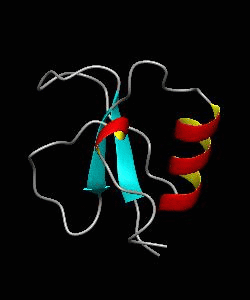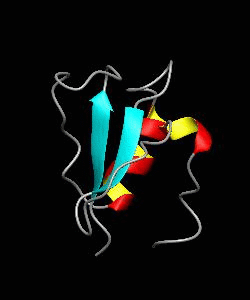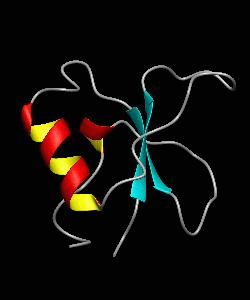
CD2BP2-GYF
T cell activation through the CD2 cell surface receptor is transmitted by proline-rich sequences within its cytoplasmic tail. Here is the solution structure of the CD2 binding domain of the novel protein CD2BP2, which we name the glycine-tyrosine-phenylalanine (GYF) domain.
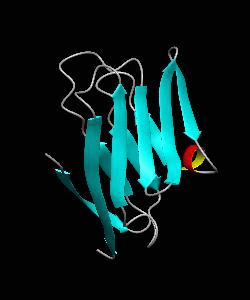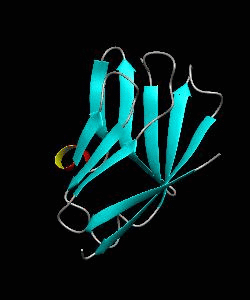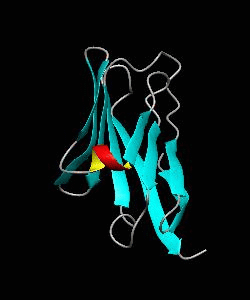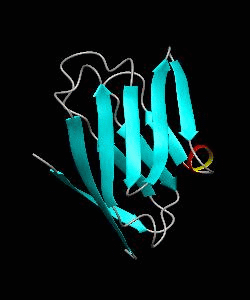
1dCD58
Cell surface receptors, such as CD58 and CD2, are responsible for faciliating immune responses. Here is the soluble 11 kDa adhesion domain extracted from the heavily glycosylated 55 kDa human CD58 ectodomain. The new structural information supports a 'hand-shake' model of CD2-CD58 interaction involving the GFCC'C" faces of both CD2 and CD58 adhesion domains.
General
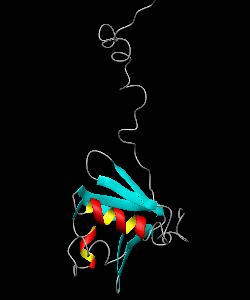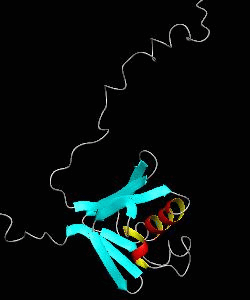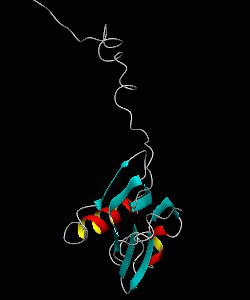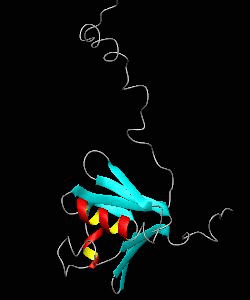
MMOB
The soluble methane monooxygenase from the pseudothermophile Methylococcus capsulatus (Bath) is a three-component enzyme system that catalyzes the selective oxidation of methane to methanol. We have used NMR spectroscopy to produce a highly refined structure of MMOB, the 16-kDa regulatory protein of this system.
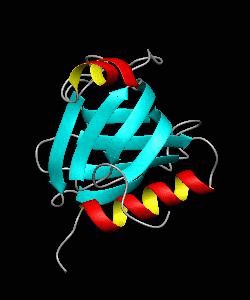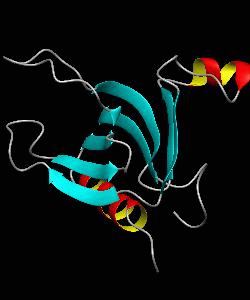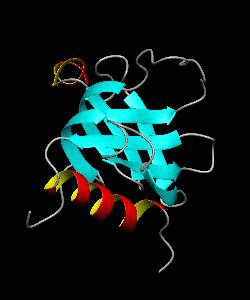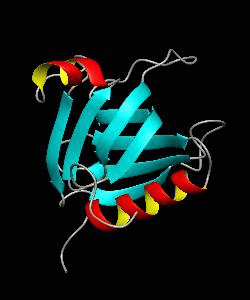
beta-spectrin PH
The pleckstrin homology (PH) domain, which is approximately 100 amino acids long, has been found in about 70 proteins involved in signal transduction and cytoskeletal function. It is conceivable that the PH domain of beta-spectrin plays a part in the association of spectrin with the plasma membrane of cells. Here we have solved the solution structure of the 122-residue PH domain of Drosophila beta-spectrin.