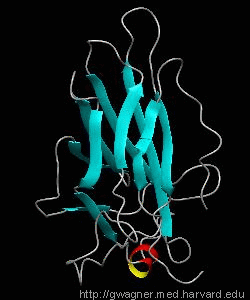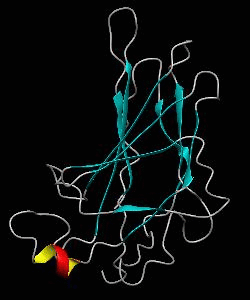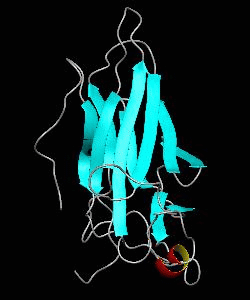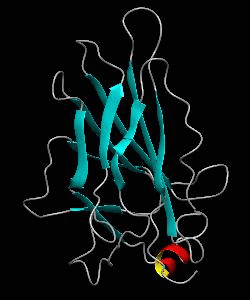
NFATc1
The nuclear factor of the activated T cell (NFAT) family of transcription factors regulates cytokine gene expression by binding to the promoter/enhancer regions of antigen-responsive genes. Here is the binary complex formed between the core DNA-binding domain of human NFATC1 and the ARRE2 DNA site from the interleukin-2 promoter.
PUT3
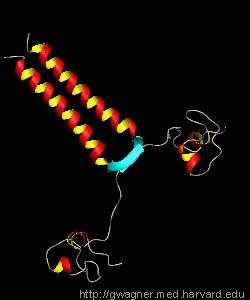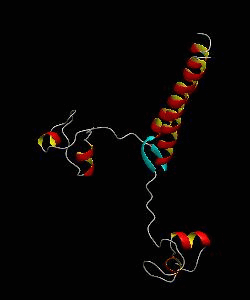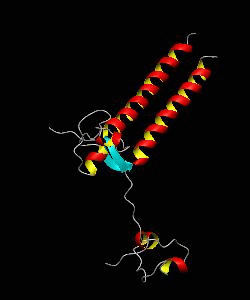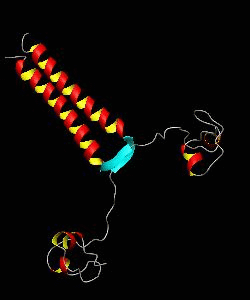
The solution structure and backbone dynamics of the transcriptional activator PUT3 (31-100) has been characterized using NMR spectroscopy. PUT3 (31-100) contains three distinct domains: a cysteine zinc cluster, linker, and dimerization domain. The cysteine zinc cluster of PUT3 closely resembles the solution structure of GAL4, while the dimerization domain forms a long coiled-coil. A comparison of the structural elements provides a model for the DNA binding specificity of this protein.
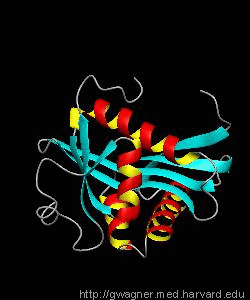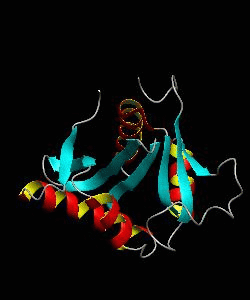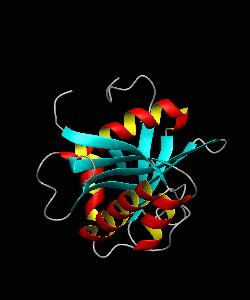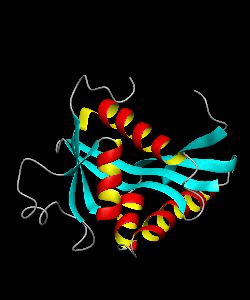
GCN5
Gene transcription requires the release of inactive DNA from its packaging of histone proteins. Yeast GCN5 is recruited to the promoter and causes hyper-acetylation of histones and transcriptional activation of target genes. Here we present the solution structure of the catalytic domain of the GCN5 histone acetyltransferase (residues 47-210) in complex with coenzyme A.